A factorial design is obtained by cross-combining of all the factors values. The number of different treatment groups that we have in any factorial design can easily be determined by multiplying through the number notation.

5 4 7 1 Full Factorial Example
5 terms necessary to understand factorial designs 5 patterns of factorial results for a 2x2 factorial designs Descriptive misleading main effects The F-tests of a Factorial ANOVA Using LSD to describe the pattern of an interaction Introduction to factorial designs Factorial designs have 2 or more Independent Variables An.
. Full factorial is 2k Fractional Factorial is 2kp Degree of fraction is 2p 25-5 Half-Fraction 2k Factorials This is one half the usual number of runs Similar to blocking procedure Choose a generator which divides efiects into two Based on pluses and minuses of one factor Deflning Relation. If the experimenter can reasonably assume that certain high-order interactions often 3-way. This would be called a 2 x 2 two-by-two factorial design because there are two independent variables each of which has two levels.
One of the big advantages of factorial designs is that they allow researchers to look for interactions between independent variables. Use a fractional factorial design. Straightforward construction if all flxed efiects In 3 factor model.
A 22 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables each with two levels on a single dependent variable. Weekly on the growth of a certain species of plant. 21 displays a two-factorial design in which each factor is represented by a single dimension.
Full factorials are seldom used in practice for large k k7. So for example a 43 factorial design would involve two independent variables with four levels for one IV and three levels for the other IV. Amount of catalyst charge 1 temperature 2 pressure 3 and concentration of one of the reactants 4.
A 2k 2 k full factorial requires 2k 2 k runs. The major features of these selected designs are that they i apply only to 2 n factorial experiments where n the number of factors is at least 5 ii involve only one half of the complete set of factorial treatment combinations denoted by 2 n-1 iii allow all main effects and two-factor interactions to be estimated. For more complex plans.
Full Factorial Design with 2 Factors and 5 Levels Six Sigma iSixSigma Forums General Forums New to Lean Six Sigma Full Factorial Design with 2 Factors and 5 Levels This topic has 18 replies 6 voices and was last updated 3 years 10 months ago by Robert Butler. DOE An example of Two-Factor Experimental Design with Replication In the last blog on DOE Two-factor factorial design we have discussed the statistical concepts and equations for the two-factor experimental design with replications. The factors form a Cartesian coordinate system ie all combinations of each level of each dimension.
Using our example above where k 3 p 1 therefore N 2 2 4. 4 FACTORIAL DESIGNS 41 Two Factor Factorial Designs A two-factor factorial design is an experimental design in which data is collected for all possible combinations of the levels of the two factors of interest. 2k-p design allows analyzing k factors with only 2k-p experiments.
In this type of design one independent variable has two levels and the other independent variable has three levels. 19-4 Washington University in St. Discuss 22 factorial designs with relevant example.
21 the first dimension is the variable that is assumed to affect the speed of processing of process. We refer to the three levels of the factors as low 0 intermediate 1 and high 2. The Advantages and Challenges of Using Factorial Designs.
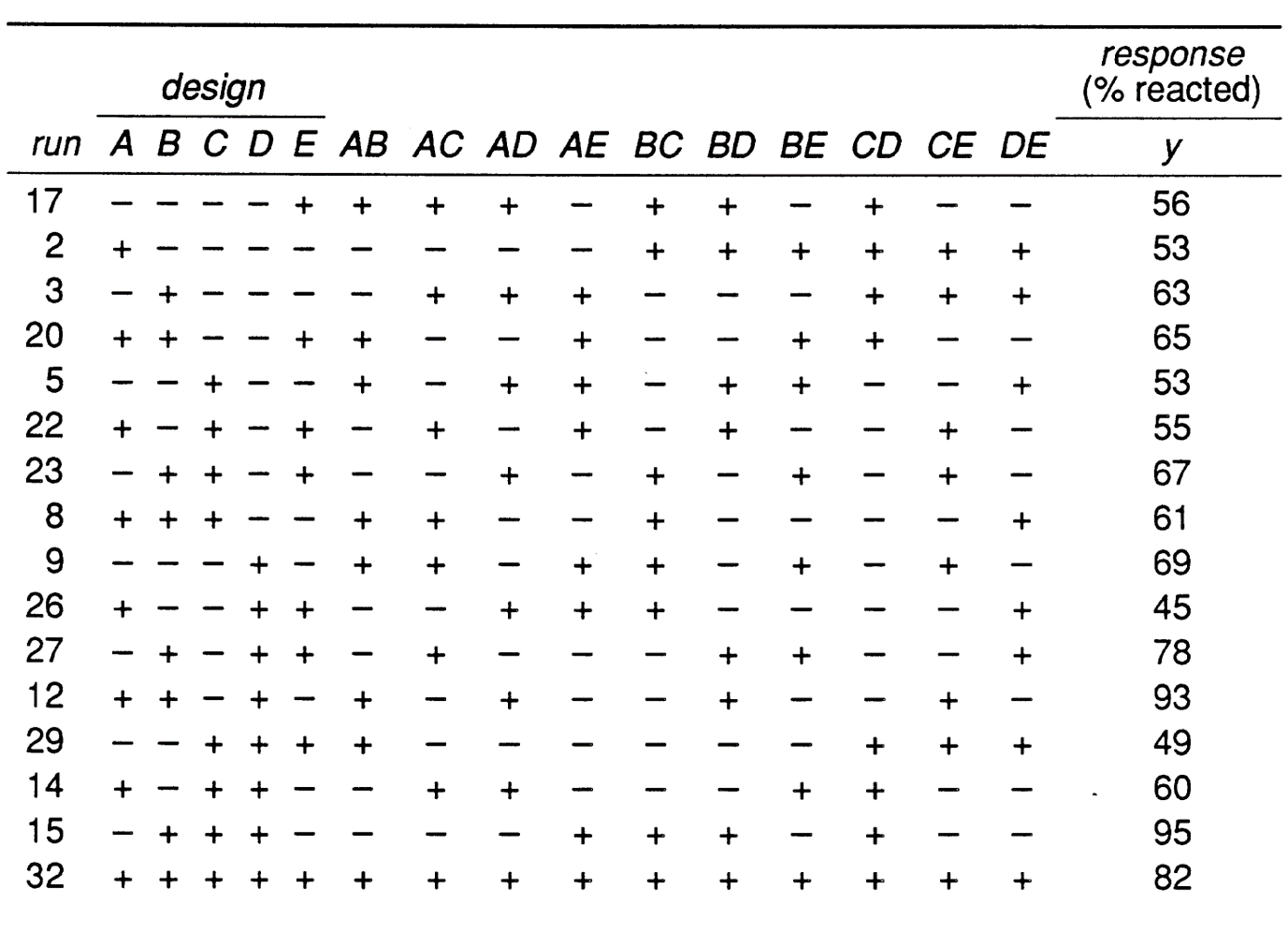
For example runs 2 and 4 represent factor A at the high level. The 3k Factorial Design is a factorial arrangement with k factors each at three levels. The response y is the percent conversion at each of the 16 run conditions.
The choice of the two levels of factors used in two level experiments depends on the factor. For economic reasons fractional factorial designs which consist of a fraction of full factorial designs are. In a typical situation our total number of runs is N 2 k p which is a fraction of the total number of treatments.
2k-2 design requires only one quarter of the experiments. If the first independent variable had three levels not smiling closed-mouth smile open-mouth smile then it would be a 3 x 2 factorial design. If equal sample sizes are taken for each of the possible factor combinations then the design is a balanced two-factor factorial design.
Louis CSE567M 2008 Raj Jain Example. 3-2 The points for the factorial designs are labeled in a standard order starting with all low levels and ending with all high levels. We can also depict a factorial design in design notation.
In our notational example we would need 3 x 4 12 groups. The design is. High and watering frequency daily vs.
For instance in our example we have 2 x 2 4 groups. So in this case either one of these. For example in a 32 design the nine treatment combinations are denoted by 00 01 10 02 20 11 12 21 22.
10112 Example - 24 design for studying a chemical reaction. 5 Two-Level Fractional Factorial Designs Because the number of runs in a 2k factorial design increases rapidly as the number of factors increases it is often impossible to run the full factorial design given available resources. Now we illustrate these concepts with a simple statistical design of experiments.
Factorial Designs III Design of Experiments - Montgomery Sections 5-4 - 5-7 16 General Factorial Model Factorial Design - observations at all possible combinations a levels of Factor A b levels of Factor B. Misuse of the ANOVA for 2k Factorial Experiments For 2k designs the use of the ANOVA is confusing and makes little sense. A fractional factorial design is useful when we cant afford even one full replicate of the full factorial design.
Partitioned into individual SS for effects each equal to Neffect24 divided by df1 and turned into an F-ratio. Study 7 factors with only 8 experiments. For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs.
The average response from these runs can be contrasted with those from runs 1. 10112 Example - 24 design for studying a. 19-5 Washington University in St.
A process development experiment studied four factors in a 24 factorial design. For example a two level experiment with three factors will require math2times 2times 2238math runs. A 23 factorial design is a type of experimental design that allows researchers to understand the effects of two independent variables on a single dependent variable.
For example suppose a botanist wants to understand the effects of sunlight low vs. A full factorial two level design with mathkmath factors requires math2kmath runs for a single replicate.

Highly Fractional Factorial Designs Reliawiki
Two Level Factorial Experiments Reliawiki

R How To Simulate An Unreplicated Factorial Design Cross Validated
Suppose The Experiment Was Ran With A Single Chegg Com

2 K Factorial Design Tool Real Statistics Using Excel

Full Factorial Design For 2 Factors And 2 Levels A Design Matrix Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments
Post a Comment